ShapeScript
Blocks
A block is a nested list of instructions, contained inside { ... } braces. Some commands, such as builders or CSG operations, accept a block parameter instead of a simple value like a number or vector.
Instructions inside a block are executed within the scope of the command that invoked them. Typically that means that any transforms or material changes made inside the block will only apply to geometry created inside the same block. This also applies to any symbols that you define inside the block.
You can define your own blocks using the define command. Here is a block that creates a five-pointed star:
define star {
path {
for 1 to 5 {
point 0 -0.5
rotate 1 / 5
point 0 -1
rotate 1 / 5
}
point 0 -0.5
}
}
You can call it by simply referencing its name, like this:
star
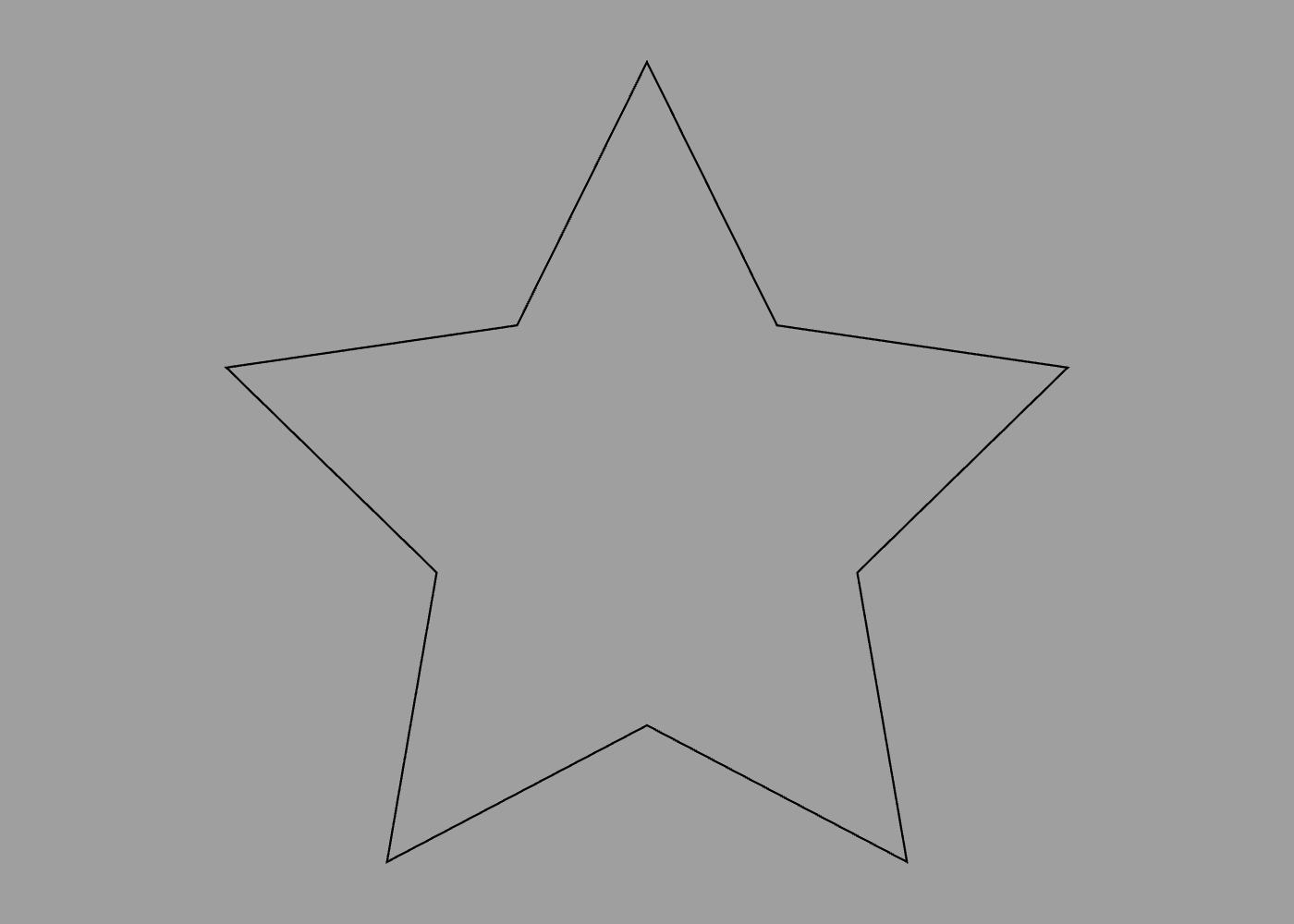
Note: There is a subtle distinction between the code above and the code below:
define star path {
for 1 to 5 {
point 0 -0.5
rotate 1 / 5
point 0 -1
rotate 1 / 5
}
point 0 -0.5
}
In the original code, we defined a new block symbol that creates a star-shaped path. In the code above we’ve defined a symbol whose value is a star-shaped path. The former code is evaluated at the point when it is called, whereas the latter code is evaluated at the point when it is defined.
The end-result is the same in this case, so it may seem like the distinction doesn’t matter, but the advantage of the former approach is that we can add options to vary the behavior of the code when it is called.
Options
To add an option to a block, you use the option command. This works in a similar way to the define command, but it allows the specified value to be overridden by the caller.
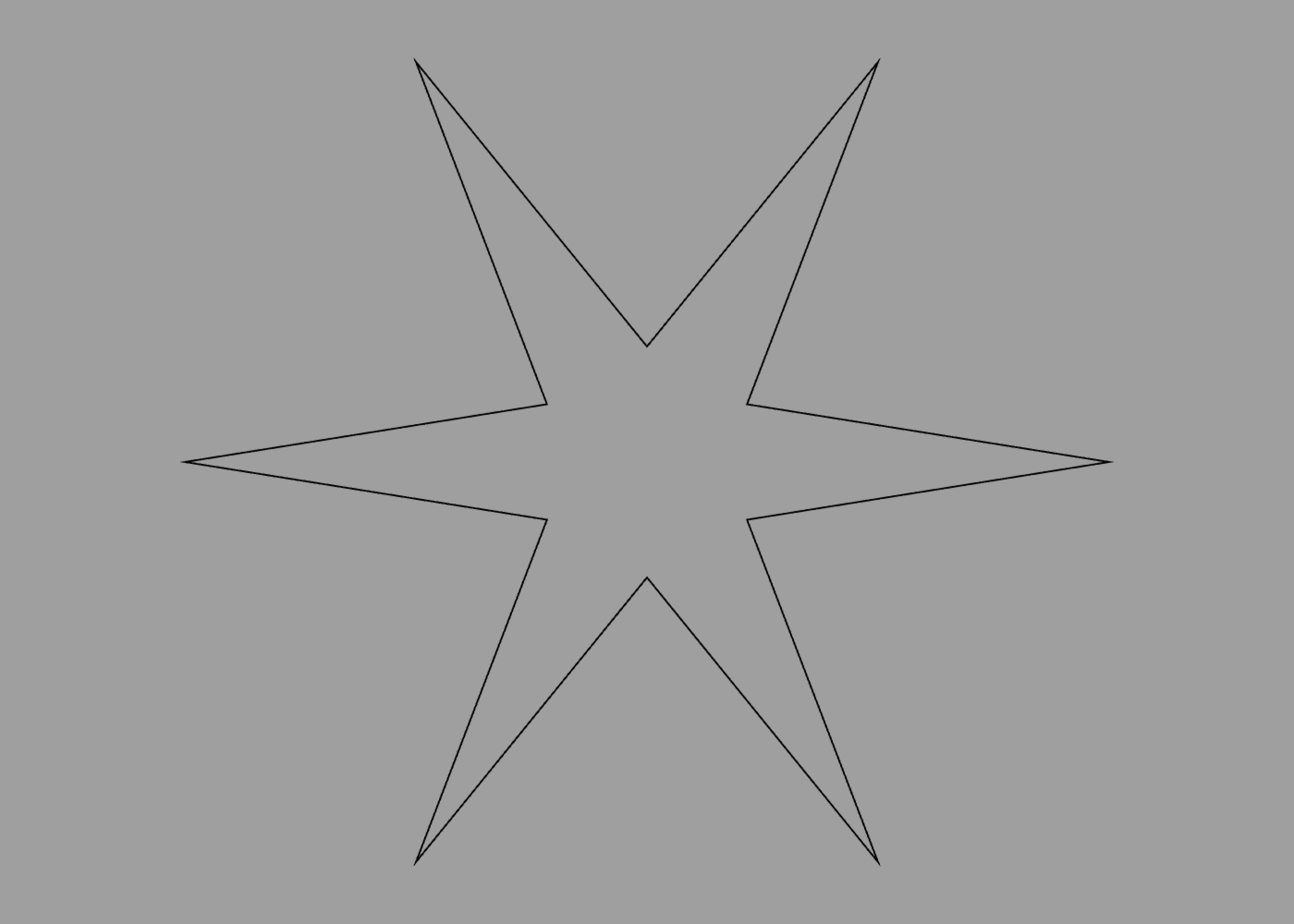
The code below extends the star definition with options for the radius and number of points:
define star {
option radius 1
option points 5
path {
for 1 to points {
point 0 -0.5
rotate 1 / points
point 0 -radius
rotate 1 / points
}
point 0 -0.5
}
}
Now we can use those options to create a star with 6 points if we choose:
star {
points 6
radius 2
}
Children
ShapeScript’s builder and csg block commands accept child shapes which they use as inputs to construct a mesh:
difference {
cube { size 1 }
sphere { size 1.1 }
}
You can do the same with your own custom blocks by using the children property. This property is available inside a block definition, and returns a tuple of whatever child objects were passed in by the caller.
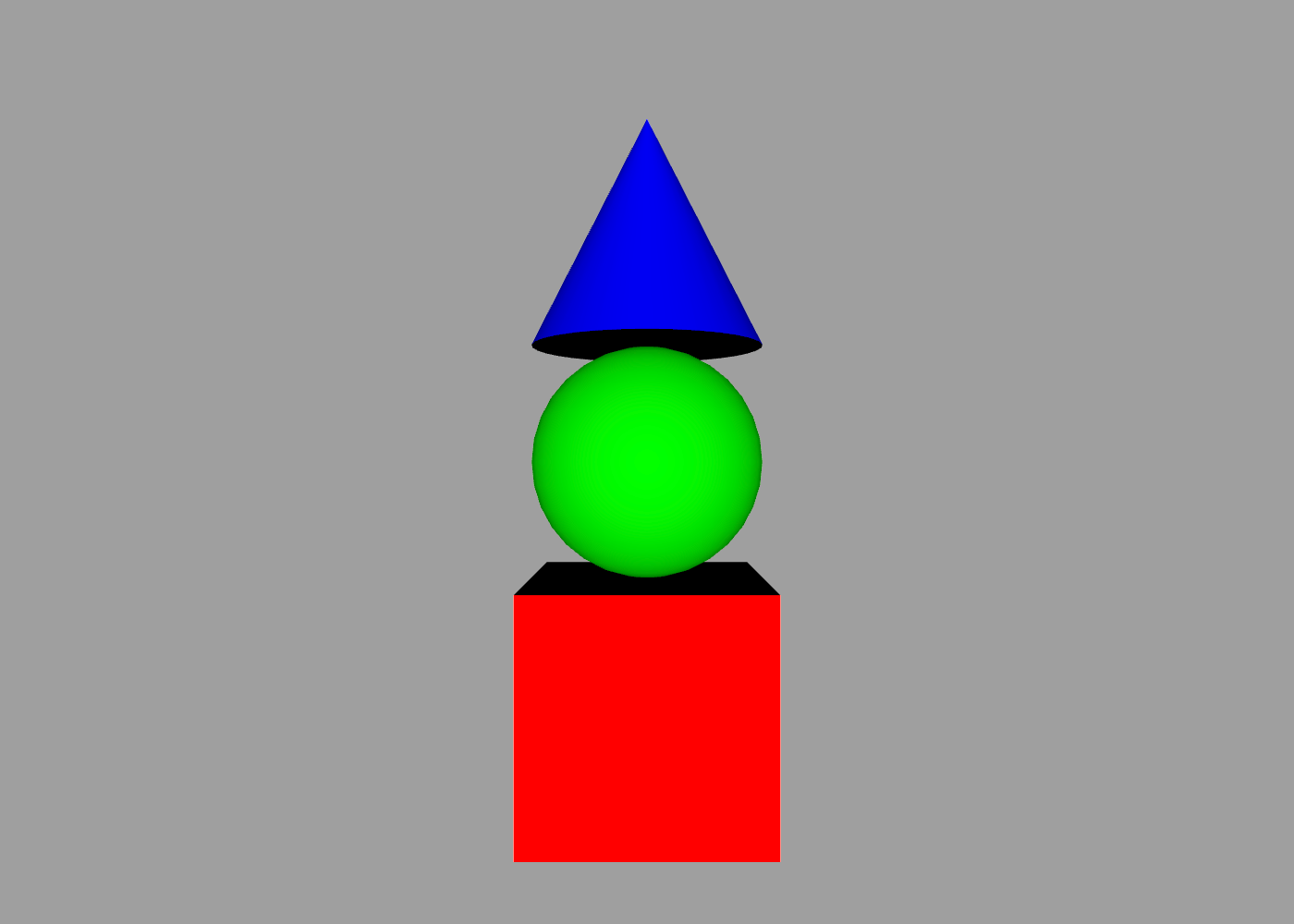
Here is a simple block that takes whatever child objects are passed in and stacks them vertically along the Y-axis:
// define reusable stack command
define stack {
for mesh in children {
mesh
translate 0 mesh.bounds.size.height
}
}
// stack some shapes
stack {
cube { color red }
sphere { color green }
cone { color blue }
}
Note: The children passed to a block can be any type, not just paths or meshes. ShapeScript uses type inference to raise an error if the caller passes children of a different type than the block expects.